This article demonstrates how to add column in dataframe using Map and Map Partitions
What is the best way to add new column to DataFrame in PySpark
Here we are going to see adding column to DataFrame using withColumn, Spark SQL and Map function.
In this scenario, not much difference between withColumn and Spark SQL, but Map create huge difference. Try to use Spark SQL wherever applicable and possible because DataFrames and Spark SQL are much more sensitive than using rdd.map
There are cases you will end up using Spark SQL UDF, during this time rdd.map will be better option for large datasets processing from my perspective If you have having better hardware you may use mapPartitions.
Let us see example on each scenario.
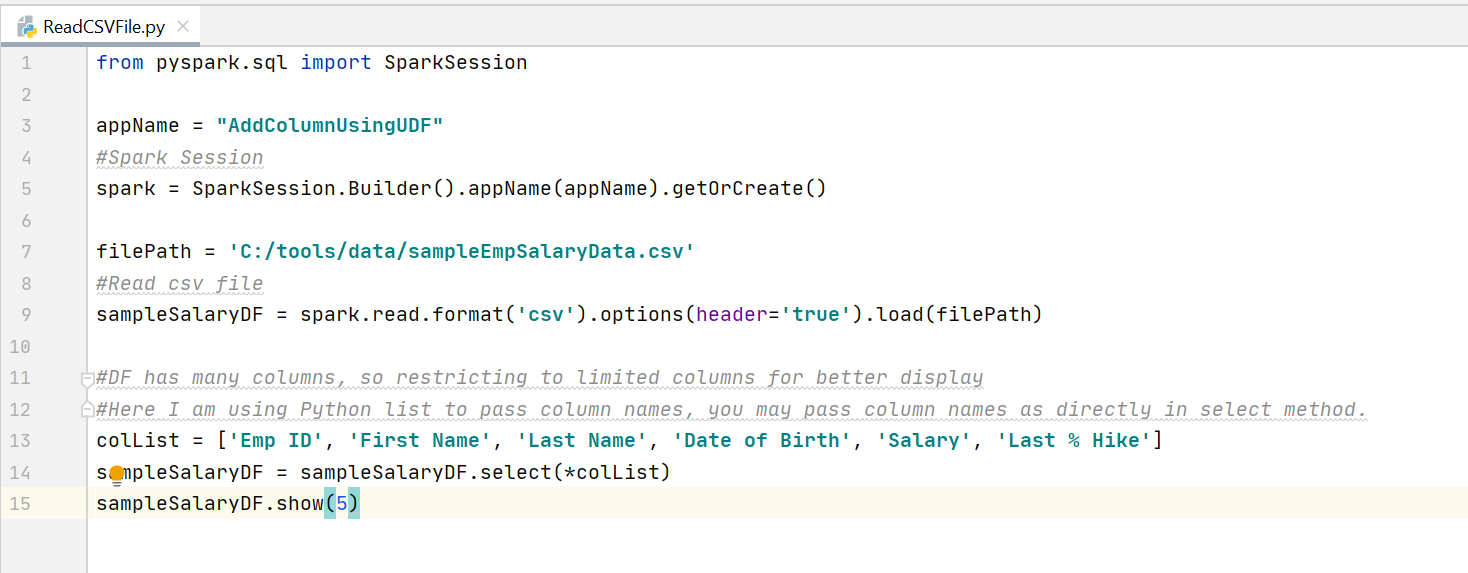
Traditional approach to add new column in DataFrame
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql.functions import *
appName = "AddColumnUsingMap"
#Spark Session
spark = SparkSession.Builder().appName(appName).getOrCreate()
filePath = 'C:/tools/data/sampleEmpSalaryData.csv'
#Read csv file
sampleSalaryDF = spark.read.format('csv').options(header='true').load(filePath)
#DF has many columns, so restricting to limited columns for better display
#Here I am using Python list to pass column names, you may pass column names as directly in select method.
colList = ['Emp ID', 'First Name', 'Last Name', 'Date of Birth', 'Salary', 'Last % Hike']
sampleSalaryDF = sampleSalaryDF.select(*colList)
sampleSalaryDF.show(5)
Output:
+------+----------+---------+-------------+------+-----------+
|Emp ID|First Name|Last Name|Date of Birth|Salary|Last % Hike|
+------+----------+---------+-------------+------+-----------+
|677509| Lois| Walker| 3/29/1981|168251| 21%|
|940761| Brenda| Robinson| 7/31/1970| 51063| 27%|
|428945| Joe| Robinson| 6/16/1963| 50155| 16%|
|408351| Diane| Evans| 12/4/1977|180294| 1%|
|193819| Benjamin| Russell| 4/17/1977|117642| 13%|
+------+----------+---------+-------------+------+-----------+
withColumn:
sampleSalaryDFUpdated = sampleSalaryDF.withColumn('New Salary', expr("Salary + (Salary * int(replace(`Last % Hike`, '%', '')) / 100)"))
sampleSalaryDFUpdated.show(5)
Output:
+------+----------+---------+-------------+------+-----------+----------+
|Emp ID|First Name|Last Name|Date of Birth|Salary|Last % Hike|New Salary|
+------+----------+---------+-------------+------+-----------+----------+
|677509| Lois| Walker| 3/29/1981|168251| 21%| 203583.71|
|940761| Brenda| Robinson| 7/31/1970| 51063| 27%| 64850.01|
|428945| Joe| Robinson| 6/16/1963| 50155| 16%| 58179.8|
|408351| Diane| Evans| 12/4/1977|180294| 1%| 182096.94|
|193819| Benjamin| Russell| 4/17/1977|117642| 13%| 132935.46|
+------+----------+---------+-------------+------+-----------+----------+
SparkSQL:
sampleSalaryDF.createOrReplaceTempView("SampleSalary")
sampleSalaryDFUpdated = spark.sql("select a.*, Salary + (Salary * int(replace(`Last % Hike`, '%', '')) / 100) as `New Salary` from SampleSalary a")
Output:
+------+----------+---------+-------------+------+-----------+----------+
|Emp ID|First Name|Last Name|Date of Birth|Salary|Last % Hike|New Salary|
+------+----------+---------+-------------+------+-----------+----------+
|677509| Lois| Walker| 3/29/1981|168251| 21%| 203583.71|
|940761| Brenda| Robinson| 7/31/1970| 51063| 27%| 64850.01|
|428945| Joe| Robinson| 6/16/1963| 50155| 16%| 58179.8|
|408351| Diane| Evans| 12/4/1977|180294| 1%| 182096.94|
|193819| Benjamin| Russell| 4/17/1977|117642| 13%| 132935.46|
+------+----------+---------+-------------+------+-----------+----------+
add new column in DataFrame: using rdd.map
from pyspark.sql.types import *
#Create Python function to add new column
def addRevisedSalary(row):
rowDict = row.asDict()
revisedSalary = float(rowDict.get("Salary")) + \
(float(rowDict.get("Salary")) *
(int(rowDict.get("Last % Hike").replace("%", "")) / 100))
rowDict["New Salary"] = str(revisedSalary)
return rowDict
#Using Map
sampleSalaryUpdRDD = sampleSalaryDF.rdd.map(addRevisedSalary)
#we need to pass updated schema while creating DataFrame
inputSchema = sampleSalaryDF.schema
newSchema = inputSchema.add("New Salary", StringType())
sampleSalaryDFUpdated = spark.createDataFrame(sampleSalaryUpdRDD, newSchema)
sampleSalaryDFUpdated.show(5)
Output:
+------+----------+---------+-------------+------+-----------+----------+
|Emp ID|First Name|Last Name|Date of Birth|Salary|Last % Hike|New Salary|
+------+----------+---------+-------------+------+-----------+----------+
|677509| Lois| Walker| 3/29/1981|168251| 21%| 203583.71|
|940761| Brenda| Robinson| 7/31/1970| 51063| 27%| 64850.01|
|428945| Joe| Robinson| 6/16/1963| 50155| 16%| 58179.8|
|408351| Diane| Evans| 12/4/1977|180294| 1%| 182096.94|
|193819| Benjamin| Russell| 4/17/1977|117642| 13%| 132935.46|
+------+----------+---------+-------------+------+-----------+----------+
add new column in DataFrame: using rdd.mapPartitions
#Create Python function to add new column for map partitions
def addRevisedSalaryUsingPartition(partition):
for row in partition:
rowDict = row.asDict()
revisedSalary = float(rowDict.get("Salary")) + \
(float(rowDict.get("Salary")) *
(int(rowDict.get("Last % Hike").replace("%", "")) / 100))
rowDict["New Salary"] = str(revisedSalary)
yield rowDict
#Using Map Partitions
sampleSalaryUpdRDD = sampleSalaryDF.rdd.mapPartitions(addRevisedSalaryUsingPartition)
#we need to pass updated schema while creating DataFrame
inputSchema = sampleSalaryDF.schema
newSchema = inputSchema.add("New Salary", StringType())
#Create DataFrame
sampleSalaryDFUpdated = spark.createDataFrame(sampleSalaryUpdRDD, newSchema)
sampleSalaryDFUpdated.show(5)
Output:
+------+----------+---------+-------------+------+-----------+----------+
|Emp ID|First Name|Last Name|Date of Birth|Salary|Last % Hike|New Salary|
+------+----------+---------+-------------+------+-----------+----------+
|677509| Lois| Walker| 3/29/1981|168251| 21%| 203583.71|
|940761| Brenda| Robinson| 7/31/1970| 51063| 27%| 64850.01|
|428945| Joe| Robinson| 6/16/1963| 50155| 16%| 58179.8|
|408351| Diane| Evans| 12/4/1977|180294| 1%| 182096.94|
|193819| Benjamin| Russell| 4/17/1977|117642| 13%| 132935.46|
+------+----------+---------+-------------+------+-----------+----------+
rdd.map operation gives better performance compare to udf for complex transformation in DataFrame.
rdd.mapPartitions is more efficient than
rdd.map if you have good infra, not much benefit using local or single node env.
Spark SQL is recommended option for DataFrame transformations, if any complex transformation which is not possible in Spark SQL (in-build functions/expressions) then you can try using rdd.map or rdd.mapPartitions.
Copyright - There is no copyright on the code. You can copy, change and distribute it freely. Just mentioning this site should be fair
(C) November 2020, manivelcode